Understanding your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is crucial when applying for a personal loan. Your DTI is a key factor lenders consider when assessing your ability to repay borrowed funds. A lower DTI generally signifies lower risk to the lender, increasing your chances of approval and potentially securing a more favorable interest rate. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to calculating your DTI, interpreting its significance, and improving your chances of loan approval by managing your debt effectively. Learn how to leverage your DTI to secure the best possible terms on your next personal loan.
This guide delves into the intricacies of the debt-to-income ratio, explaining how it’s calculated using your monthly debt payments and your gross monthly income. We’ll cover various types of debt included in the calculation, addressing common misconceptions and providing practical strategies for improving your DTI. Whether you’re seeking a personal loan for debt consolidation, home improvements, or other personal needs, understanding your DTI is a fundamental step towards securing a favorable loan offer. Mastering your DTI empowers you to navigate the world of personal finance with greater confidence and achieve your financial goals.
What Is Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio?
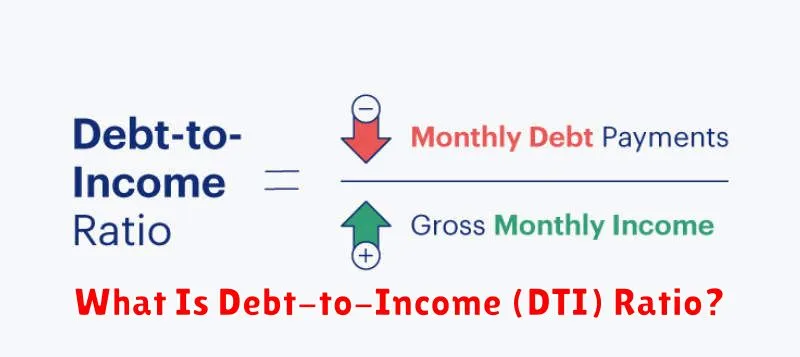
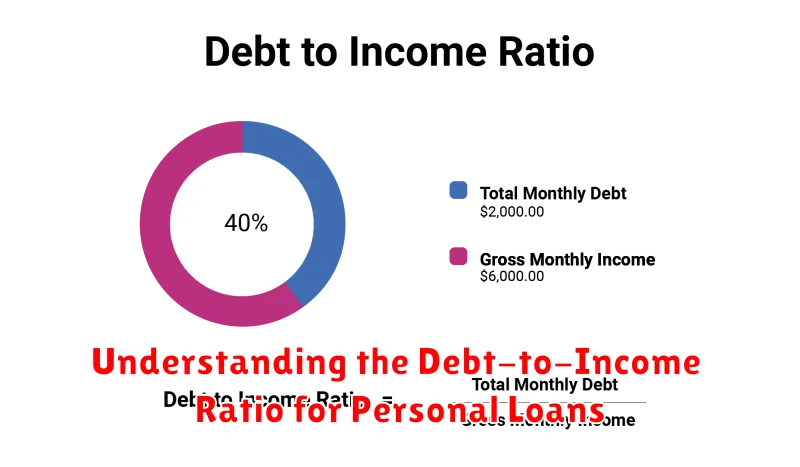
The debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial financial metric used by lenders to assess your ability to repay a loan. It’s a simple calculation that compares your total monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income.
A lower DTI ratio generally signifies a lower risk to the lender. This is because a smaller portion of your income is already committed to debt payments, leaving more available to cover new loan obligations.
Calculating your DTI involves adding up all your monthly debt payments – including credit card payments, student loans, car loans, and mortgage payments – and dividing that total by your gross monthly income (before taxes).
For example, if your total monthly debt payments are $2,000 and your gross monthly income is $6,000, your DTI ratio would be 33.33% ($2,000 / $6,000 = 0.3333). This is often expressed as a percentage.
Different lenders have varying DTI thresholds for loan approval. Some may prefer a DTI ratio below 36%, while others may accept applicants with a higher DTI, depending on the type of loan and other factors, such as your credit score and credit history. A lower DTI ratio often qualifies you for better interest rates and loan terms.
Understanding your DTI is essential when applying for personal loans. By knowing your DTI, you can better assess your borrowing power and make informed decisions about your financial goals.
How DTI Affects Loan Eligibility
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial factor lenders consider when assessing your loan application. It represents the percentage of your monthly gross income that goes towards paying off your existing debts. A lower DTI generally indicates a lower risk to the lender, making you a more attractive borrower.
Lenders use DTI to gauge your ability to manage additional debt. A high DTI suggests you may be already stretched financially, making it more challenging to repay a new loan. This can lead to loan rejection or, if approved, less favorable terms such as a higher interest rate or smaller loan amount. Conversely, a low DTI demonstrates financial responsibility and a greater capacity to handle additional debt, thus increasing your chances of approval and potentially securing better loan terms.
The specific DTI threshold for loan approval varies among lenders and loan types. Some lenders may be more flexible with higher DTIs, particularly if other aspects of your financial profile are strong, such as a high credit score and a stable income history. However, it’s generally advisable to maintain a DTI below 43% to improve your eligibility for favorable loan options.
Understanding your DTI is vital in the loan application process. Before applying, calculating your DTI can help you determine your eligibility and manage expectations. If your DTI is high, consider strategies to lower it before applying, such as paying down existing debts or increasing your income. This proactive approach significantly enhances your chances of securing a loan with favorable terms.
Ideal DTI Ranges for Most Lenders
Understanding your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is crucial when applying for a personal loan. Lenders use your DTI to assess your ability to repay the loan while managing your existing debts. A lower DTI generally indicates a lower risk to the lender.
While specific DTI requirements vary among lenders and loan types, most lenders prefer applicants with a DTI below 43%. This is often considered the threshold for approval for many personal loans. However, some lenders may be more lenient, while others may have stricter requirements, particularly for larger loan amounts.
For those with DTIs between 43% and 50%, securing a personal loan might still be possible, though it could be more challenging. Lenders may require a higher interest rate or additional collateral to mitigate the perceived risk. The approval process may also be more rigorous.
Applicants with a DTI exceeding 50% typically face significant difficulty obtaining personal loans. Lenders view a high DTI as a high risk of default. In such cases, it’s recommended to work on reducing your debt before applying for a loan. Focusing on paying down existing debts can significantly improve your DTI and increase your chances of approval in the future.
It’s important to remember that these are general ranges. Your individual circumstances, credit score, and the type of loan you’re applying for will also influence a lender’s decision. Always check with individual lenders for their specific DTI requirements before applying for a personal loan.
How to Calculate Your DTI Before Applying

Understanding your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is crucial before applying for a personal loan. A strong DTI demonstrates your ability to manage debt responsibly, significantly impacting your loan approval chances and the interest rates offered.
Calculating your DTI involves two key figures: your monthly debt payments and your gross monthly income. To determine your monthly debt payments, add up all your recurring monthly obligations, including:
- Minimum credit card payments: Include all outstanding credit card balances.
- Auto loan payments: The monthly amount due on any car loans.
- Student loan payments: The monthly payments for all student loans.
- Mortgage payments: If applicable, include your monthly mortgage payment.
- Other loan payments: This encompasses any other installment loans you may have.
Next, determine your gross monthly income. This is your total income before taxes and other deductions. If you’re self-employed, use your average monthly net profit. For employed individuals, use your pre-tax monthly salary or wages.
Finally, to calculate your DTI, divide your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income and multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. For example, if your total monthly debt payments are $1,000 and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your DTI is ($1,000/$5,000) * 100 = 20%.
It’s important to note that lenders have different DTI thresholds for loan approval. Generally, a lower DTI is preferred. Knowing your DTI beforehand allows you to assess your borrowing capacity and make informed decisions about applying for a personal loan.
Ways to Lower DTI for Better Approval Odds
A low debt-to-income ratio (DTI) significantly improves your chances of loan approval. Lenders use DTI to assess your ability to manage repayments alongside existing financial obligations. A lower DTI demonstrates a greater capacity to handle additional debt, making you a less risky borrower.
One effective strategy is to pay down high-interest debt. Prioritize credit cards and other high-interest loans. Even small, consistent payments can make a difference over time, reducing your overall debt and subsequently lowering your DTI.
Consider consolidating debt. Combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate can simplify repayments and potentially lower your monthly payments. This can lead to a significant reduction in your DTI, showcasing improved financial management to lenders.
Increasing your income is another powerful way to lower your DTI. Seeking a raise, taking on a side job, or finding a higher-paying position can all boost your income, leading to a lower DTI ratio without altering your debt level.
Careful budgeting and expense tracking are crucial. Identifying areas where you can cut back on spending can free up funds to allocate toward debt repayment, accelerating the reduction of your DTI. Small changes in spending habits can have a substantial impact over time.
Finally, avoid taking on new debt while working to improve your DTI. Applying for new credit cards or loans can negatively impact your score and increase your DTI, hindering your progress. Focus on reducing existing debt before considering new borrowing.
How DTI Impacts Interest Rates
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial factor that lenders consider when assessing your eligibility for a personal loan and determining the interest rate you’ll receive. DTI represents the percentage of your monthly gross income that goes towards paying your existing debts. A lower DTI generally indicates a lower risk to the lender, resulting in a more favorable interest rate.
Lenders use DTI as a key indicator of your ability to manage additional debt. A high DTI suggests that a significant portion of your income is already allocated to debt repayment. This increases the lender’s perception of risk, as it raises concerns about your capacity to make timely payments on a new loan. Consequently, they may offer a higher interest rate to compensate for the increased risk or even deny your application altogether.
Conversely, a low DTI signals to lenders that you have a greater capacity to handle additional debt. This lower risk profile makes you a more attractive borrower, leading to potentially lower interest rates and improved loan terms. A strong DTI showcases responsible financial management, increasing your chances of loan approval and securing a more favorable interest rate.
It’s important to note that the impact of DTI on interest rates isn’t uniform across all lenders. Different lenders have varying risk tolerance levels and may weigh DTI differently in their assessment. However, a lower DTI consistently improves your chances of securing a more competitive interest rate.
Therefore, before applying for a personal loan, it is beneficial to calculate your DTI and explore strategies to improve it if it’s high. This may involve paying down existing debts, increasing your income, or a combination of both. By improving your DTI, you significantly enhance your prospects of obtaining a personal loan with a favorable interest rate.