Facing unexpected medical expenses can be financially devastating. Many individuals find themselves needing quick access to funds to cover urgent medical bills, such as hospital stays, surgeries, or expensive medications. A personal loan might seem like a viable solution, offering a lump sum to address immediate needs. However, before you take out a personal loan for medical expenses, it’s crucial to understand the potential implications and explore all available options. This article will guide you through the key considerations to help you make an informed decision regarding your medical debt and the use of personal loans.
Understanding the interest rates, repayment terms, and hidden fees associated with a personal loan is paramount. Carefully evaluating your financial situation and exploring alternative financing options, such as medical credit cards, healthcare payment plans, or crowdfunding, is essential to prevent further financial strain. We’ll analyze the pros and cons of using a personal loan for medical bills, helping you determine if it’s the right choice for your specific circumstances and empowering you to navigate the complexities of medical financing effectively.
Why Some People Use Personal Loans for Health Bills
High medical costs are a significant concern for many individuals in the United States. Unexpected illnesses or injuries can quickly lead to overwhelming medical bills, far exceeding what many people can afford to pay out-of-pocket.
Health insurance, while crucial, often leaves a substantial gap in coverage. High deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-network expenses can create a financial burden that even those with insurance struggle to manage. This leaves many searching for alternative financing options.
Personal loans offer a potential solution for covering these unexpected medical expenses. They provide a lump sum of money that can be used to pay for various medical costs, including hospital stays, surgeries, treatments, and prescription medications. The loan amount can be tailored to the specific financial need, offering flexibility in managing the debt.
In some cases, using a personal loan may be preferable to other options such as high-interest credit cards. Personal loans typically offer lower interest rates than credit cards, leading to lower overall interest payments and a quicker debt repayment.
Furthermore, consolidating various medical bills into a single personal loan can simplify the payment process, making it easier to track and manage debt. This consolidated approach allows for a more manageable repayment schedule, preventing further financial stress.
However, it is crucial to carefully consider the implications before taking out a personal loan for medical expenses. Understanding the interest rates, repayment terms, and potential long-term financial impact is vital before making a decision.
Comparing Loan vs Payment Plans from Providers
When facing significant medical expenses, many individuals explore financing options. Two common choices are personal loans from lenders and payment plans offered directly by healthcare providers. Understanding the key differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Provider payment plans often involve structuring your total bill into smaller, manageable installments. These plans are typically interest-free or carry a significantly lower interest rate than other financing options. However, they’re usually limited to the specific provider’s services and may have restrictions on the amount you can finance or the length of the repayment period. Eligibility might also be subject to the provider’s internal credit assessment.
In contrast, personal loans offer greater flexibility. You can borrow a larger sum, and repayment terms tend to be longer, providing more manageable monthly payments. Lenders offer a wider range of interest rates, but these rates are typically higher than provider payment plans. Your eligibility for a personal loan depends on your credit score and financial history, meaning you’ll need to meet certain requirements established by the lender. The application process also involves more scrutiny, and approval isn’t guaranteed.
Interest rates are a critical factor to consider. While provider payment plans often boast lower or no interest, the overall cost could potentially be higher if the repayment period is short and the amount financed is smaller compared to what a personal loan could offer. Personal loans, while generally having higher interest rates, provide the flexibility to potentially borrow more at a fixed rate over a longer term.
Ultimately, the best option depends on your individual circumstances and the specifics of your medical bill. Carefully evaluate the terms and conditions, including interest rates, repayment periods, fees, and eligibility requirements, of both provider payment plans and personal loans before making a decision.
Understanding Loan Terms Before Medical Use

Before using a personal loan for medical expenses, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the loan terms. Failing to do so could lead to unexpected financial burdens and complicate an already stressful situation.
Interest rates are a primary consideration. Compare rates from multiple lenders to secure the most favorable terms. A lower interest rate will translate to lower overall costs over the life of the loan. Pay close attention to whether the rate is fixed or variable, as a variable rate can fluctuate and increase your monthly payments.
The loan term, or repayment period, significantly impacts your monthly payment amount. Longer loan terms result in lower monthly payments but increase the total interest paid over time. Shorter terms mean higher monthly payments but less interest paid overall. Carefully evaluate your budget to determine the most manageable monthly payment.
Fees associated with the loan, such as origination fees, late payment fees, and prepayment penalties, can add significantly to the total cost. Make sure to inquire about all potential fees upfront and factor them into your overall cost analysis. Some lenders may offer loans with no origination fees, making them more attractive.
Understanding the repayment schedule is essential. Know precisely when payments are due and how much each payment will be. Many lenders offer online account access to track payments and view loan details. Establish a budget that comfortably accommodates your monthly loan payment to avoid delinquency.
Finally, be aware of any requirements the lender may have. This can include minimum credit score requirements, income verification, and collateral requirements. Meeting these requirements is essential for loan approval. If you have a low credit score, explore options such as secured loans or loans with co-signers to improve your chances of approval.
How to Estimate Total Cost of Borrowing
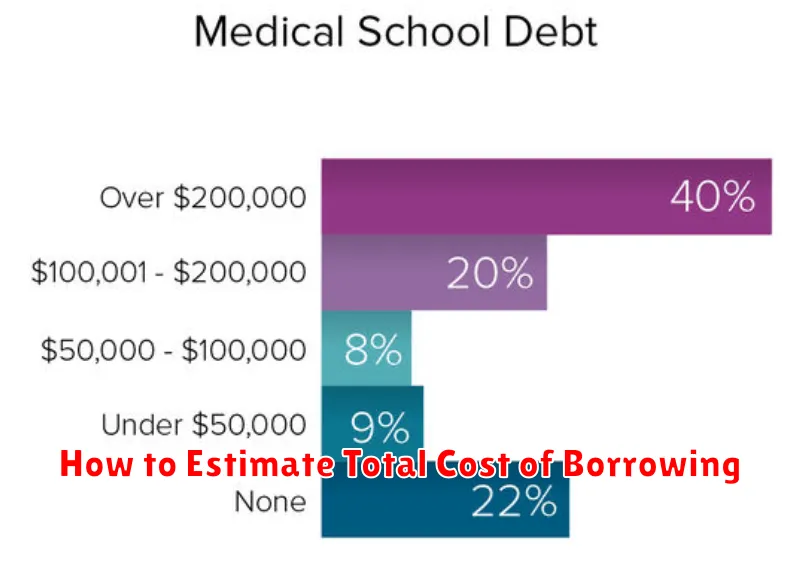
Before you take out a personal loan for medical expenses, it’s crucial to accurately estimate the total cost of borrowing. This goes beyond just the principal loan amount; it involves understanding all associated fees and charges.
First, determine the loan amount you need to cover your medical bills. This should be a precise figure, factoring in all anticipated costs, including doctor’s visits, hospital stays, medications, and therapies. Don’t forget to account for potential unexpected expenses.
Next, identify the interest rate. This is expressed as a percentage and represents the cost of borrowing the money. Lenders will provide you with an annual percentage rate (APR), which incorporates the interest rate along with other fees. The APR is a key indicator of the loan’s true cost.
Then, find out the loan term, or the length of time you have to repay the loan. This is typically expressed in months or years. A longer loan term will result in lower monthly payments but a higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. A shorter loan term means higher monthly payments but less interest paid in total.
Many lenders offer loan calculators on their websites. These tools allow you to input the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term to calculate your estimated monthly payment and the total amount repaid (principal plus interest). Utilize this resource to understand the full financial commitment.
Finally, don’t forget to factor in any additional fees, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, or late payment fees. These charges can significantly increase the overall cost of borrowing. Be sure to ask your lender about all potential fees upfront.
By carefully considering these factors, you can arrive at a realistic estimate of the total cost of borrowing, allowing you to make an informed decision about whether a personal loan is the right financial solution for your medical expenses.
Questions to Ask Lenders About Health-Related Loans
Securing a loan for medical expenses requires careful consideration and thorough research. Before committing to any lender, it’s crucial to ask specific questions to ensure you understand the terms and conditions fully. This proactive approach can save you from potential financial difficulties down the line.
One of the most important aspects to clarify is the interest rate. Inquire about the Annual Percentage Rate (APR), which includes all fees and interest charges. Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the most competitive rate. Ask if the rate is fixed or variable, as a variable rate can fluctuate, potentially increasing your repayments.
Understand the loan repayment terms. Ask about the loan term length, which dictates how long you have to repay the loan. Longer terms mean lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid, while shorter terms mean higher monthly payments but lower overall interest. Clarify the repayment schedule, including due dates and payment methods.
It’s vital to inquire about any fees associated with the loan. Ask about origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. These fees can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan. A detailed breakdown of all costs will give you a clearer picture of the total expense.
Explore the lender’s requirements and eligibility criteria. Ask about the necessary documentation, credit score requirements, and income verification processes. Understanding these requirements beforehand will help you prepare adequately and avoid delays in loan processing.
Finally, ask about the lender’s customer service and support. Inquire about their contact information, accessibility, and their process for handling inquiries or issues related to your loan. A responsive and supportive lender can make a significant difference during the loan repayment process.
Alternatives to Consider Before Borrowing
Before taking out a personal loan for medical expenses, explore alternative financing options. These may offer more favorable terms or avoid the need for debt altogether.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you have an HSA, funds contributed pre-tax can be used for qualified medical expenses, offering a tax-advantaged way to cover costs. Check your HSA balance and eligibility before proceeding with a loan.
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): Similar to HSAs, FSAs allow pre-tax contributions for medical expenses. However, FSAs usually have stricter usage deadlines and may not cover as many expenses as an HSA. Consider your FSA balance and the timeframe for using the funds.
Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs): Offered by some employers, HRAs reimburse employees for eligible medical expenses. Inquire with your HR department about your company’s HRA plan and its potential contribution towards your medical bills.
Negotiating Medical Bills: Don’t hesitate to negotiate directly with healthcare providers or hospitals. Many are willing to work with patients to create payment plans or reduce outstanding balances. A payment plan might be a more manageable solution than a loan.
Crowdfunding Platforms: Platforms like GoFundMe allow individuals to raise funds from friends, family, and the broader community. This option can be effective for significant medical expenses but requires transparency and comfort with public fundraising.
Charitable Organizations: Numerous charitable organizations offer financial assistance for medical expenses. Research organizations relevant to your specific medical needs to determine eligibility criteria and application procedures.
Family and Friends: Consider borrowing from trusted family members or friends. While this can be a less formal arrangement, ensure clear terms and repayment agreements to maintain positive relationships.

